Ques.41. The main features of electric traction is
- High mechanical strength
- Low starting torque
- Low overload capacity
- All of the above
Answer.1. High mechanical strength Explanation:- The general features of the electric motors used for traction purpose are: Mechanical features A traction motor must be mechanically strong and robust and it should be capable of withstanding severe mechanical vibrations. The traction motor should be completely enclosed type when placed beneath the locomotive to protect against dirt, dust, mud, etc. In overall dimensions, the traction motor must have a small diameter, to arrange easily beneath the motor coach. A traction motor must have minimum weight so the weight of locomotive will decrease. Hence, the load carrying capability of the motor will increase. Electrical features High-starting torque:- A traction motor must have high-starting torque, which is required to start the motor on load during the starting conditions in urban and suburban services. Speed control:- The speed control of the traction motor must be simple and easy. This is necessary for the frequent starting and stopping of the motor in traction purpose Dynamic and regenerative braking:- Traction motors should be able to provide easy simple rheostatic and regenerative braking subjected to higher voltages so that the system must have the capability of withstanding voltage fluctuations. Temperature:- The traction motor should have the capability of withstanding high temperatures during transient conditions. Overload capacity:- The traction motor should have the capability of handling excessive overloads. Parallel running:- In traction work, more number of motors need to run in parallel to carry more load. Therefore, the traction motor should have such speed-torque and current-torque characteristics and those motors may share the total load almost equally.Special features of traction Motor
The following data is given for 42-45
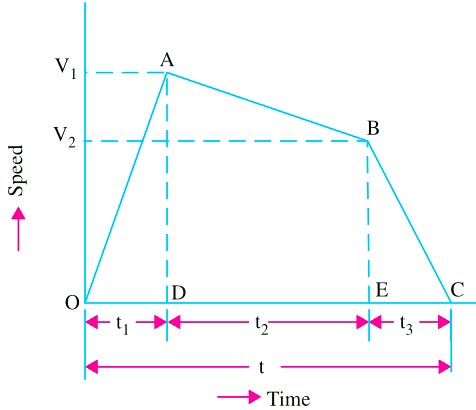
Ques.42. The speed time curve for a local train is shown in Figure. In this AB represents
- Coasting
- Acceleration
- Braking
- Regeneration
Answer.1. Coasting Explanation:- The above diagram represents the speed-time curve of suburban service. The AB represent the coasting period. In suburban service, the distance between two adjacent stops for an electric train is lying between 1 and 8 km. In this service, the distance between stops is more than the urban service and smaller than the mainline service. The typical speed—time curve for suburban service is shown in Fig. The speed—time curve for urban service consists of three distinct periods they are: (i) Acceleration. (ii) Coasting. (iii) Retardation. For this service, there is no free-running period. The coasting period is comparatively longer since the distance between two stops is more. Braking or retardation period is comparatively small. It requires relatively high values of acceleration and retardation. Typical acceleration and retardation values are Iying between 1.5 and 4 kmph and 3 and 4 kmph, respectively.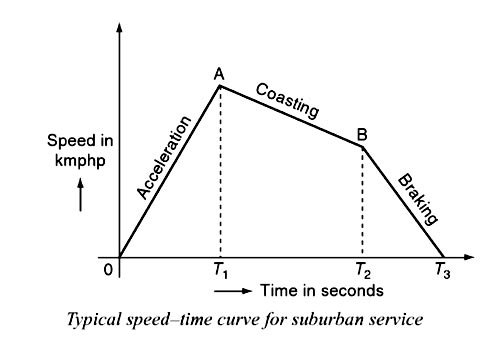
Ques.43. From the figure, it can be concluded that
- The rate of acceleration is the same as the rate of acceleration during braking
- The average acceleration is zero
- Time taken during coasting is equal to the time during acceleration and braking
- No free running period
Answer.4. No free running period Explanation:- In suburban service, the distance between stops is more than the urban service and smaller than the mainline service. In this case, the distance between stops averages from 3 to 5 km over a distance of 25 to 30 km from the city terminus. Here, also, high rates of acceleration and retardation are necessary. Since the distance between the two stations is small therefore there is no running period.
Ques.44. The area under the curve represents
- Average speed
- Average acceleration
- Net acceleration
- Distance traveled
Answer.4. Distance traveled Explanation:- The area under the speed time curve gives the distance traveled during, given time internally and slope at any point on the curve toward abscissa gives the acceleration and retardation at the instance, out of the two speed—time curve is more important.
Ques.45. The duration for braking is represented by the time
- 0 – t1
- 0 – t2
- t2 – t3
- t1 – t2
Answer.3. t2 – t3 Explanation:- The duration of braking is represented by t2 – t3. In suburban service braking or retardation, the period is comparatively small. It requires relatively high values of acceleration and retardation. Typical acceleration and retardation values are Iying between 1.5 and 4 kmph and 3 and 4 kmph, respectively.
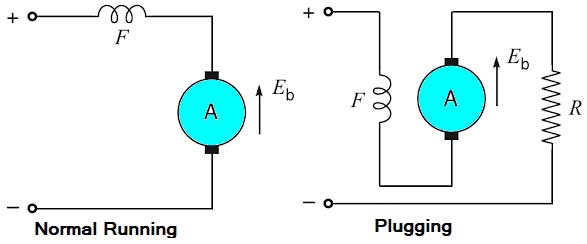
Ques.46. __________ method is called reverse current braking
- Plugging
- Rheostatic
- Mechanical braking
- Regenerative braking
Answer.1. Plugging Explanation:- The disadvantages of this method are: 1. The kinetic energy of the motor is dissipated in the external resistance in the form of heat. So, this method of braking is inefficient. 2. The braking in this method fails in case of failure of the supply.Plugging
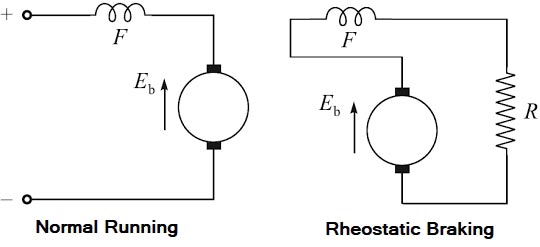
Ques.47. __________ method is called reverse current braking
- Plugging
- Rheostatic
- Mechanical braking
- Regenerative braking
Answer.2. Rheostatic Explanation:- The disadvantage of the method is that the kinetic energy of the motor is dissipated as heat in the resistance and it is a wastage. The armature current and so the magnetic field changes with the change in speed. Therefore, the speed-torque curve is not linear in case of the series motor.Rheostatic braking
Ques.48. Which method is the most efficient method of electrical braking
- Plugging
- Rheostatic
- Mechanical braking
- Regenerative braking
Answer.4. Regenerative braking Explanation:- In regenerative braking, the motor is not disconnected from the supply but is made to run as a generator by utilizing the Kinetic energy of the moving train. Electrical energy is feedback to the supply. The magnetic drag produced on account of generator action offers the braking torque. It is the most efficient method of braking. Advantages:- Following are the advantages of regenerative braking: Disadvantages:Regenerative braking
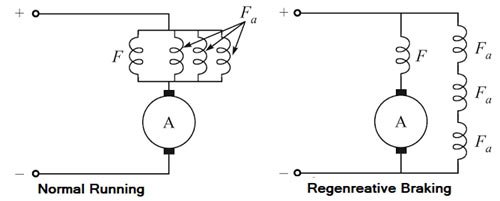
Ques.49. The advantages of electrical braking over mechanical braking
- More reliable
- More economical
- Smooth operation
- All of the above
Answer.4. All of the above Explanation:- The process of bringing the motor to rest within the predetermined time is known as braking. A good braking system must have the following features: Braking applied to bring the motor to rest position is of two types and they are: 1. Electric braking. Mechanical braking In this process of braking, the kinetic energy of the rotating parts is dissipated in the form of heat by the brake shoes of the brake lining that rubs on a wheel of vehicle or brake drum. Electric braking In this process of braking, the kinetic energy of the rotating parts of the motor is converted into electrical energy which in turn is dissipated as heat energy in resistance or in sometimes, electrical energy is returned to the supply. Here, no energy is dissipated in brake shoes. Saving; no replacement cost: In case of mechanical braking, due to friction there is excessive wear on brake lining which needs frequent and costly replacement. But in electric braking, no such replacement is required hence saves money.
2. Mechanical braking.Advantages of the electric braking over the mechanical braking
Disadvantages of the electric braking
Ques.50. For 600 V dc line for tramcars
- The track is connected to negative of the supply
- The track is connected to positive of the supply
- The track is connected to the mid-voltage of 300 V
- None of the above
Answer.1. The track is connected to negative of the supply Explanation:- We use 25kv ac supply which runs in overhead lines. Now pentagraph is the device which is used to give that supply to train. The overhead catenary wire acts as a positive supply. The tracks below are earthed via each of the electric poles on the side of the tracks. The positive of the wire goes via resistor banks to the positive point on the motor. The negative terminal of the motor is connected to the locomotive’s wheel assembly which passes the current to the earth via tracks i.e the rails acts as a return conductor(negative terminal). Current flows only when the circuit is closed and there should be a potential difference and ground is neutral so it closes the circuit.
FOR ILLUMINATION MCQ CLICK HERE
FOR MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION SYSTEM MCQ CLICK HERE
FOR HEATING AND WELDING MCQ CLICK HERE
FOR TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM MCQ CLICK HERE
FOR DC MOTOR MCQ CLICK HERE
FOR 3-Φ INDUCTION MOTOR MCQ CLICK HERE
FOR SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR OR ALTERNATOR MCQ CLICK HERE
FOR Electric Drive MCQ CLICK HERE



Nice