Ques.81. Thermal conductivity is least for
- Air
- Water
- Glass
- Copper
Answer.1. Air Explanation:- Thermal conductivity is the property of a material to conduct heat. The thermal conductivity of air at 25°C is 0.0262 W/(m K) The thermal conductivity of water at 25°C is 0.606 W/(m K) The thermal conductivity of glass at 25°C is 1.05 W/(m K) The thermal conductivity of copper at 25°C is 401 W/(m K) Hence Copper has the highest thermal conductivity
Ques.82. Which method of heating is likely to give leading power factor?
- Electric arc heating
- Induction heating
- Dielectric heating
- Resistance heating
Answer.3. Dielectric heating Explanation:- Dielectric heating, also known as electronic heating, RF (radio frequency) heating, and high-frequency heating, is the process in which a high-frequency alternating electric field, radio wave, or microwave electromagnetic radiation heats a dielectric material. Dielectric heating (also called High-frequency capacitive heating) is employed for heating insulators like wood, plastics, ceramics, etc. A non-conducting material generates heat when subjected to an alternation electric field. This process wherein heating takes place due to dielectric loss is known as dielectric heating. The amount of heat produced depends on the value of the dielectric strength of the material. The non-conducting material acts as the job which is to be heated. This method is extensively used in the plastic and wood industries. It is especially of immense utility where multiple woods are to be heated and glued. The heat supplied by this method is applied even] throughout the whole body. This method is also employed in the textile, rubber, chemical, and food industries. The phenomenon of the dielectric loss taking place in insulating materials is just analogous to the hysteresis loss taking place in the magnetic materials. Just as there is no perfect conductor, so there is no perfect insulator too. If an ac voltage is applied across a piece of an insulator, an electric current i flows as shown in Fig. The total current i can be supposed to be made up of two components ic and iR as shown in Fig. where ic is the capacitive current leading the applied voltage Vin by 90° and iR is the resistive current in phase with the applied voltage Vin, as shown in Fig. The resulting dielectric loss appears in the form of heat in the dielectric of the capacitor. It is convenient to regard this i2R current as flowing through a leakage resistance R placed in parallel with the capacitance C as shown in Fig. The current flowing in the circuit is given by Ic = E/Xc Where Ic = Current flowing through the capacitor in Amp E = High-frequency supply voltage Xc = Capacitive reactance in Ohm During the charging and discharging of the capacitor, the molecular arrangement of the job changes because of the continuous stress created by the electric field. This change in molecular arrangement results in the generation of heat. When a solid dielectric material (Insulating) is subjected to an alternating electric field, it is not supposed to carry any current. However, in practice, some leakage current passes through it and power loss is takes place. This loss is called the dielectric loss and result in heating of the dielectric material.Dielectric heating
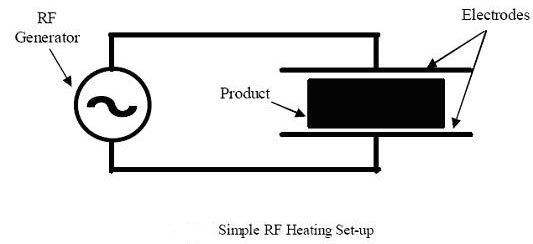
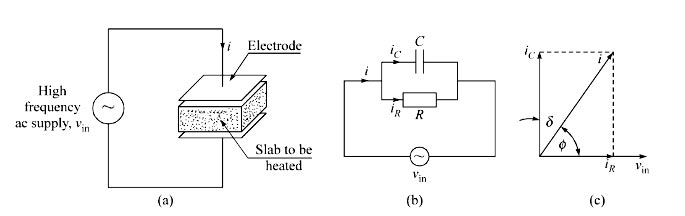
Ques.83. Direct resistance heating is used in
- Electrode Boiler
- Salt-Bath furnace
- Resistance Welding
- All of the above
Answer.4. All of the above Explanation:- Direct resistance heating (or ohmic heating) is based on the flow of an electrical current through the body to be heated, which is directly connected to an electrical supply. The heating can be realized by DC or AC currents, but the industrial applications are mostly done with alternating ones. Materials with fairly high electrical resistivity, such as carbon and low alloy steels and nickel alloys, are readily heated by direct resistance. With low resistivity materials such as copper and aluminum, the process is often not cost-effective. Direct resistance heating is used in the iron and steel industry: for heating rods and billets prior to rolling and forging for ferrous and non-ferrous annealing; either alone or i^l combination with other fuels for melting glass; in electrode boilers, for water heating and steam raising; and in salt baths for the surface heat treatment of metallic components.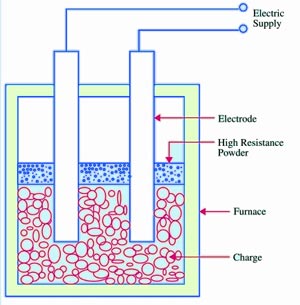
Ques.84. Which of the following method is suitable for heating of conduction medium?
- Radiant heating
- Eddy current heating
- Induction heating
- Indirect arc heating
Answer.3. Induction heating Explanation:- Induction heating is defined as the process of heating an electrically conducting object (usually a metal) by electromagnetic induction, through heat generated in the object by eddy currents. In induction heating when an alternating voltage applied to an induction coil (e.g., solenoid coil) will result in an alternating current in the coil circuit. An alternating coil current will produce in its surroundings a time-variable magnetic field that has the same frequency as the coil current. That magnetic field strength depends on the current flowing in the induction coil, the coil geometry, and the distance from the coil. The changing magnetic field induces eddy currents in the workpiece located inside the coil. These induced currents have the same frequency as the coil current; however, their direction is opposite to the coil current. Alternating eddy currents induced in the workpiece produce their own magnetic fields, which have opposite directions in the direction of the main magnetic field of the coil. Therefore, the total magnetic field of the induction coil is a result of the source magnetic field and induced magnetic fields. Alternating eddy currents produce heat by the Joule effect (I2R). A conventional induction heating system that consists of a cylindrical load surrounded by a multiturn induction, the coil is shown in Figure.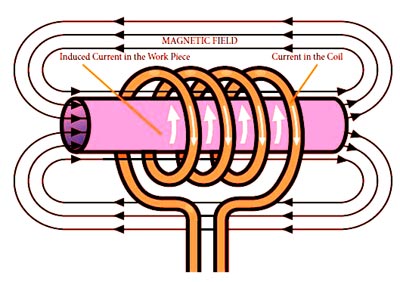
Ques.85. In dielectric heating, current flows through
- Metallic conductor
- Ionic discharge between dielectric medium and the metallic conductor
- Dielectric
- Air
Answer.3. Dielectric Explanation:- Dielectric heating, also known as electronic heating, RF (radio frequency) heating, and high-frequency heating, is the process in which a high-frequency alternating electric field, or radio wave or microwave electromagnetic radiation heats a dielectric material. A non-conducting material generates heat when subjected to an alternation electric field. This process wherein heating takes place due to dielectric loss is known as dielectric heating. The amount of heat produced depends on the value of the dielectric strength of the material. The non-conducting material acts as the job which is to be heated. This method is extensively used in the plastic and wood industries. The phenomenon of the dielectric loss taking place in insulating materials is just analogous to the hysteresis loss taking place in the magnetic materials. Just as there is no perfect conductor, so there is no perfect insulator too.
Ques.86. Which of the following is the desirable property of resistance heating elements materials?
- High resistivity
- High melting point
- Low-temperature coefficient
- All of the above
Answer.4. All of the above Explanation:- Property of resistance heating Indirect resistance furnaces use many different types of heating elements for producing heat. A good heating element should have the following properties:
Ques.87. Which of the following is the ideal method of heating plastics?
- Oil fired furnace
- Resistance furnace heating
- Dielectric heating
- Coal-fired furnace
Answer.3. Dielectric heating Explanation:- In non-magnetic materials, i.e. insulators such as China glass, ceramics, etc. are subjected to high voltage alternating current, their temperature will increase after some time. The increase in temperature is due to the conversion of dielectric loss into heat. For obtaining the adequate heating effect, the high voltage at about 20 kV and frequency in the range of 1 and 50 MHz are usually employed. The phenomenon of the dielectric loss taking place in insulating materials is just analogous to the hysteresis loss taking place in the magnetic materials. The amount of heat produced depends on the value of the dielectric strength of the material. The non-conducting material acts as the job which is to be heated. This method is extensively used in the plastic and wood industries.
Ques.88. If f be the frequency then the dielectric loss is proportional to
- f
- f2
- 1/f
- 1/f2
Answer.1. f Explanation:- The expression of the dielectric loss is given as Ploss = 2π.f.C.V2.δ Where f = frequency C = Capacitance of the capacitor V = applied voltage δ = Phase angle This power is converted into heat. Since for a given insulator material, C and δ are constant, the dielectric loss is directly proportional to V2f. That is why the high-frequency voltage is used in dielectric heating. Generally, A.C voltage of about 20 kV at a frequency of 10-30 MHz is used. The dielectric loss is proportional to frequency.
Ques.89. When E is the voltage impressed on the dielectric, the dielectric loss will be proportional to
- E
- E2
- 1/E
- 1/E2
Answer.2. E2 Explanation:- The expression of the dielectric loss is given as Ploss = 2π.f.C.E2.δ Where f = frequency C = Capacitance of the capacitor E = applied voltage δ = Phase angle This power is converted into heat. Since for a given insulator material, C and δ are constant, the dielectric loss is directly proportional to E2f. That is why the high-frequency voltage is used in dielectric heating. Generally, A.C voltage of about 20 kV at a frequency of 10-30 MHz is used.
Ques.90. Mica is a:-
- Insulating and dielectric material
- Dielectric material but not an insulator
- Insulating material but not dielectric
- Magnetic Material
Answer.1. Insulating and dielectric material Explanation:- When two conducting plates are brought closer and are separated by another plate that is made up of insulating material leads to the formation of the capacitor. The insulating material used in it is balled dielectric material. The main function of dielectric material is to store electrical energy. Thus dielectric materials are used in capacitors. There are four types of capacitors available depending on the dielectric material used in them. 1. Capacitors with air and gases as dielectric:- Such capacitors are used in circuits where energy loss in them should be low as well as the value of capacitance should be small. Thus, these types of capacitors are used in circuits where accuracy is the prime concern, for example, radio-frequency circuits. 2. Capacitors with mineral oil as dielectric:- These capacitors give a large value of capacitance with a small amount of dielectric loss. 3. Capacitors with a combination of solid and liquid as dielectric Paper, glass, mica, mineral oil, castor oil, etc. are used in these types of capacitors. Oil impregnated paper dielectric is used for making capacitors that should have a large value of capacitances. These types of capacitors are used in power distribution systems. 4. Capacitors with only solid as dielectric such as glass, mica, etc. These capacitors are used in laboratories. Mica has a high dielectric constant, high dielectric strength, and low dielectric loss. Further, the dielectric constant of mica does not change much with temperature. Most of the capacitors are constructed as sealed components.




good
Nice
Knowledgeable
Its Usefull
Amazing mcq it is always help full of exams