11. Find the output voltage for a differential amplifier, Where Vin->Induced input noise.
A. VO= -[(RF/R1)×Vd]+Vno
B. VO= -(RF/R1)×(Vd/Vno)
C. VO= -[(RF/R1)×Vd]-Vno
D. VO= -[(RF/R1)×Vd]×Vno
12. When does the op-amp said to operate in a common-mode configuration?
A. When the input voltage is equal
B. When the input voltage is equal to the output voltage
C. When the same voltage is applied to both input terminals of an op-amp
D. When different voltage is applied to both input and terminal of an op-amp
13. Common mode voltage gain of an op-amp is generally
A. >1
B. =1
C. <1
D. None of the mentioned
14. Define the common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) of op-amp?
A. CMRR=AD/ACM
B. CMRR=ACM/ AD
C. CMRR=VOCM/ACM
D. CMRR=AD*ACM
15. Find the correct equation for common-mode rejection ratio
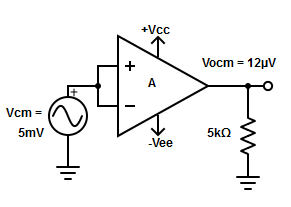
A. CMRR = 20log(AD/ ACM)
B. CMRR = 20log(Vio/ VCM)
C. CMRR = (AD* VCM)/ VOCM
D. All of the mentioned
16. When an op-amp exhibits poor common-mode rejection?
A. Small common-mode output voltage
B. Large common-mode output voltage
C. Negligible common-mode output voltage
D. None of the mentioned
17. Higher value of the common-mode rejection ratio can be reached
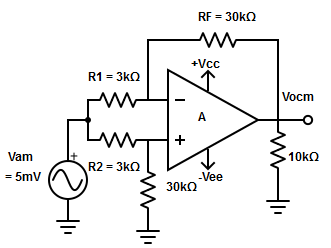
A. By reducing the common-mode voltage
B. By decreasing the differential gain
C. By reducing the common-mode input voltage
D. All of the mentioned
18. Variation in the operating frequency of op-amp causes
A. Variation in gain amplifier
B. Variation in gain phase angle
C. Variation in gain amplitude and its phase angle
D. None of the mentioned
19. A graph of the magnitude of the gain versus frequency is called
A. Break frequency
B. Frequency response plot
C. Frequency stability plot
D. Transient response plot
20. In the frequency response plot, the frequency is expressed in
A. Anti-logarithmic scale
B. Logarithmic scale
C. Linear scale
D. Exponential scale
