Pentavalent Impurity atoms that are connected to intrinsic semiconductors are called
Right Answer is:
Donor or N-type impurity
SOLUTION
- When a small amount of pentavalent impurity (having 5 valence electrons) is added to a pure semiconductor, it is known as the n-type semiconductor.
- An N-Type semiconductor is created by adding pentavalent impurities like phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), or antimony (Sb), bismuth.
- A pentavalent impurity is called a donor because it is ready to give a free electron to a semiconductor. The impurities are called dopants.
- The addition of pentavalent impurity provides a large number of free electrons in the semiconductor crystal.
- The purpose of doing this is to make more charge carriers, or electrons available in the material for conduction.
- In n-type semiconductors the number of electrons is more than the holes, so electrons are measured as majority charge carriers and holes are referred to as minority charge carriers.
Consider a pure germanium crystal. We know that the germanium atom has four valence electrons. When a small amount of pentavalent impurity like arsenic is added to the germanium crystal, a large number of free electrons become available in the crystal. The reason is simple. Arsenic is pentavalent Eel, its atom has five valence electrons.
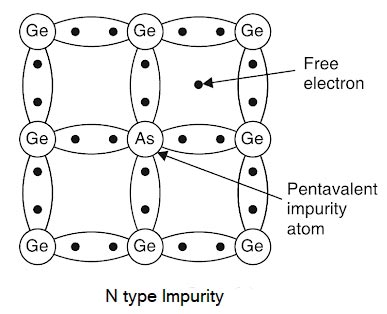
An arsenic atom fits in the germanium crystal in such a way that its four valence electrons form covalent bonds with four germanium atoms. The fifth valence electron of the arsenic atom finds no place in covalent bonds and is thus free as shown in Fig. Therefore, each arsenic atom provides one free electron, yet an extremely small amount of impurity provides enough atoms to supply millions of free electrons.
